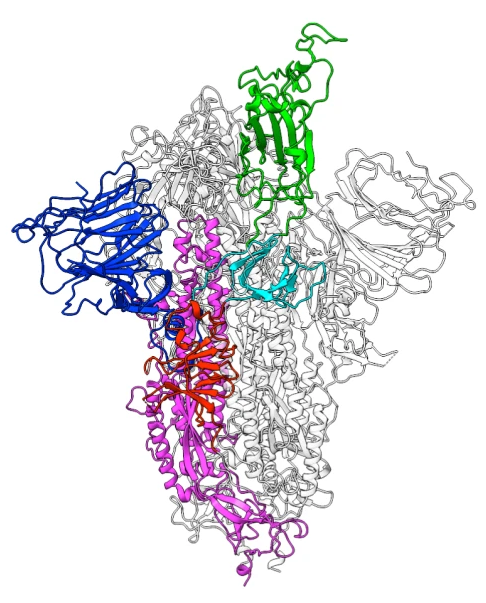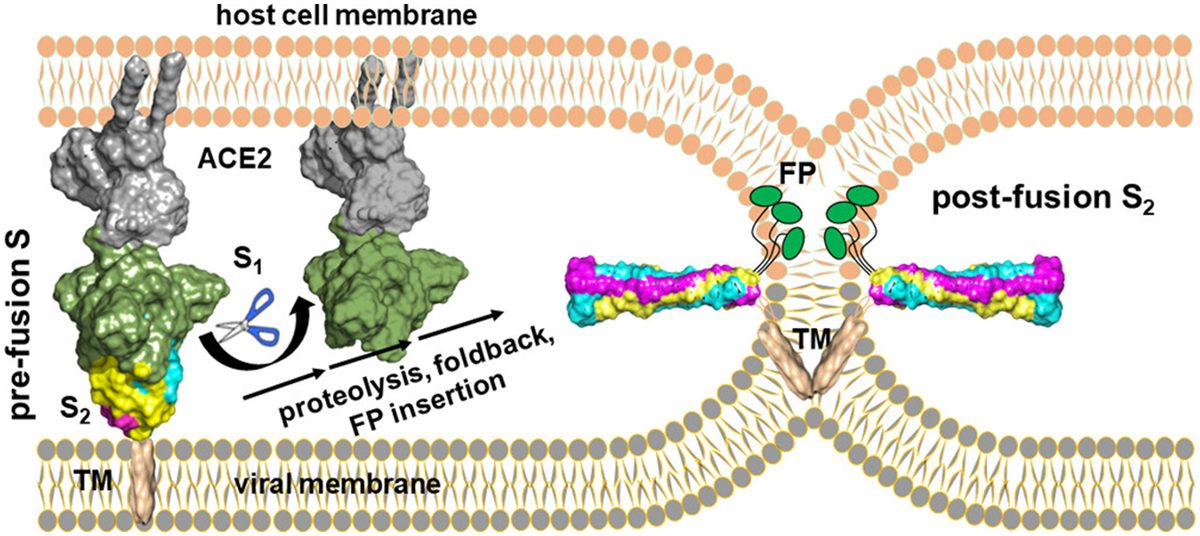
Virus entry steps. (1) Receptor ACE2 recognition by the spike protein. (2) Refolding of the S2 subunit in the spike protein after the ACE bound S1 subunit is dissociated. (3) Lipid mixing between the host membrane and the viral membrane. This step completes the virus entry, releasing the viral RNA genome into the host cytoplasm to initiate replication. (Koppisetti et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 33, 13205–13211)
Deputy Investigator

Michael Farzan, Ph.D

Deputy Investigator

Hyeryun Choe, Ph.D

Co-Investigators and Other Significant Contributors (OSC)

Fang Li, Ph.D: University of Minnesota

Asim Debnath, Ph.D: New York Blood Center, OSC

Lijun Rong, Ph.D: University of Illinois Chicago

Lanying Du, Ph.D: Georgia State University

Irina Gaisana, Ph.D: University of Illinois Chicago

Binghe Wang, Ph.D: Georgia State University

Mukesh Kumar, Ph.D: Georgia State University

Norton Peet, Ph.D: Consultant, OSC