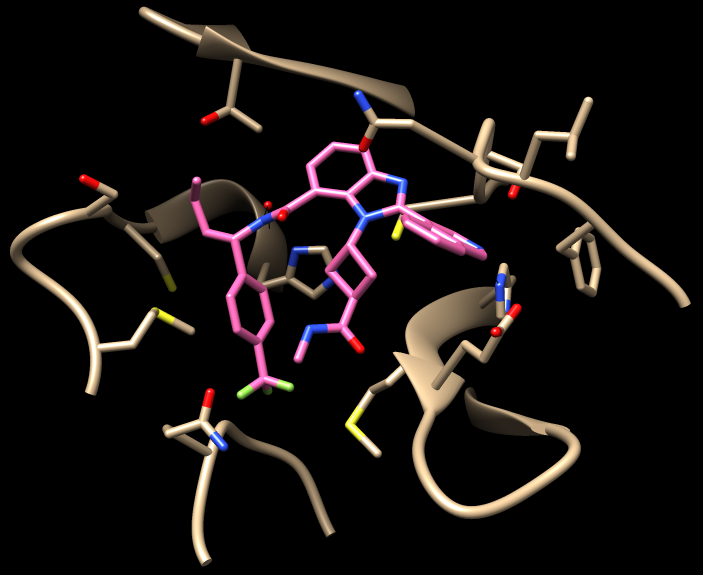
DNA-encoded chemical libraries yield non-covalent and non-peptidic SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors
Conventional structure-based design of Mpro inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 often starts from the structural information of Mpro and their binders; however, the continual rise of resistant strains requires innovative routes to discover new inhibitors. Here, the authors develop a DNA-encoded chemical library screening to produce non-covalent, non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro independently of preliminary knowledge regarding suitable starting points.
Read the whole paper HERE
Or download the pdf:
Jimmidi, R., Chamakuri, S., Lu, S. et al. DNA-encoded chemical libraries yield non-covalent and non-peptidic SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Communications Chemistry 6, 164 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-023-00961-y
