Discovery of novel SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) small molecule inhibitors for future COVID-19 antiviral development
Shaun Olsen, PhD (University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio) and Tony Huang, PhD (NYU Grossman School of Medicine).
Despite unprecedented vaccine efforts, the COVID-19 pandemic has continued to rage, leading to millions of hospitalizations and deaths globally and countless economic losses. The primary reason for this is the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as Delta and Omicron, that have increased transmissibility, virulence, and reduced effectiveness of vaccines. The continuous evolution of new viral variants necessitates searching for new antiviral strategies.
In line with the Midwest AViDD Center to develop new drugs targeting essential viral processes, this project focuses on the papain-like protease (PLpro), the other essential protease involved with SARS-CoV-2 viral replication. Currently, there are no clinical drugs that work against PLpro. The project will collaborate with Midwest AViDD Center Project 3 and use Core B’s High-Throughput Screening and DNA-Encoded Chemistry Technology (DEC-Tec) capabilities. Previously, the collaboration between Olsen and Huang yielded the first SARS-CoV-2 PLpro crystal structure during the early days of the pandemic.
Inhibition of this protease would severely compromise viral replication, viral maturation and overcome the suppression of host innate immune responses, making PLpro a viable SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drug target.

Targeting novel nsp16/nsp10 surfaces for efficient blocking of 2’-O methylation of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA
Yogesh Gupta, PhD (University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio).
Gupta studies how the nsp16-nsp10 enzyme complex of SARS-CoV-2 modifies and shields its messenger RNA to hide inside host cells. The resulting viral RNA mimics the host RNAs, subverts the host's immune response, and helps the virus hijack the host's protein synthesis machinery. Gupta's work has discovered new critical features of this mechanism that novel small molecules can selectively block.
There are no specific nsp16-nsp10 inhibitors yet available.
Gupta's unique approach is aimed at blocking the assembly of SARS-CoV-2 nsp16-nsp10 for treating patients infected with new and emerging variants of concern. A successful outcome of this project will develop broad-spectrum antivirals that can block a major pathway consisting of 2’-O-methylation of viral mRNA. Since other RNA viruses rely upon the same pathway, Gupta's approach, if successful, can be developed as a broad-spectrum antiviral agent capable of combatting several viruses belonging to different viral families.
Results from this innovative application will make transformative advances in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA modification and establish a solid platform to develop novel therapeutics for treating SARS-CoV-2. The results will also inform whether the new agents can be used as a monotherapy or can synergize the antiviral efficacy of polymerase and/or protease inhibitors (combinatorial therapy) being developed at the Midwest AViDD.
Structure-guided inhibition of Lassa virus nucleoprotein interactions with polymerase and RNA
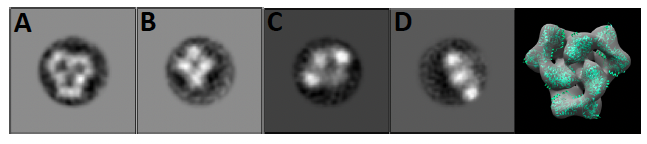
NP complexes for stable structures that can be imaged using negative stain electron microscopy. A-D) 2D class averages of hexameric (A, B) and trimeric (C, D) NP complexes. E) 3D reconstruction of particles corresponding to class A with 6 monomers of Lassa virus NP (PDB: 3mwp) docked in the density.
Ryan Abdella, PhD (University of Minnesota).
Lassa virus, an RNA virus of the arenavirus family with high pandemic potential, requires a nucleoprotein (NP) and large RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L) for transcription and replication of the viral genome. This project proposes to use cryo-electron microscopy to solve the structures of the viral genome and how NP is displaced by the polymerase and retained during transcription. These structures and complexes will be used for high throughput screening of small molecules, preventing this complex formation and inhibiting viral replication.
Abdella will be mentored by Hideki Aihara (U of M) for his project. The ambitious project aims to develop antivirals to treat an endemic disease that kills over 5,000 annually in West Africa and infects over 400,000.
This project addresses many significant, unanswered questions in arenavirus biology. It aims to provide a new platform to develop new drugs against these viral proteins to improve patient outcomes after infection.
In-situ High-resolution Imaging of the Effects of Novel Antivirals
Luiza Mendonça, PhD (University of Minnesota).
Mendonça's project will determine an antiviral's mechanism of action, validate its structure, and investigate the toxicity of compounds produced by the Midwest AViDD Center. The cryo imaging of virus-infected cells treated with compounds using cryotomography will be essential for a compound to advance to the candidate drug stage.
This Mentored Project will use a high-resolution in-situ imaging approach under frozen-hydrated conditions. This approach will determine the mechanism of action of compounds, reveal how they disrupt the viral replicative cycle, and determine potential off-target effects that were not anticipated. This goal is highly complementary to the aims of the Midwest AViDD Center and is widely applicable to all projects.
In addition, a new postdoctoral researcher will be sought to spearhead this project under the supervision of Mendonça, adding two new investigators to the Midwest antiviral community. Finally, the Principal Investigator (PI) is committed to enhancing the highly collaborative nature of the Midwest AViDD Center by providing opportunities for trainees of other groups to work with the PI in in-situ imaging techniques.
Inhibitors of Lassa Virus Endonuclease
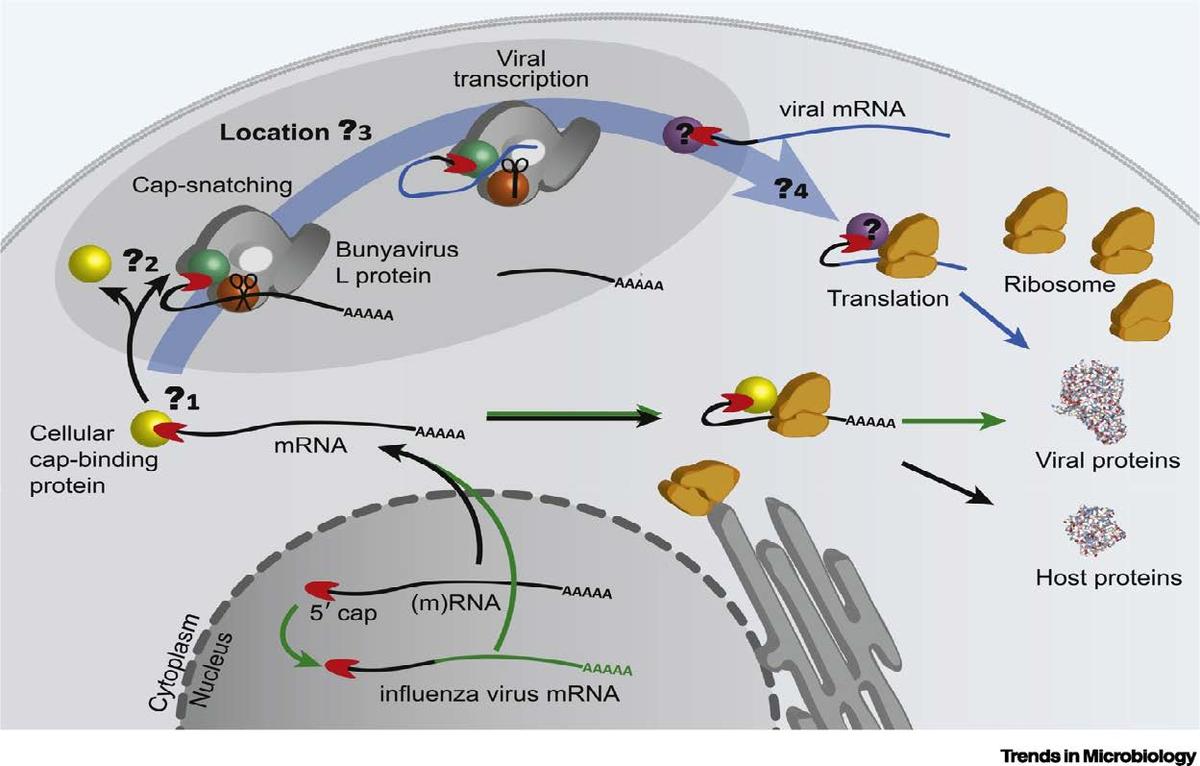
The “cap snatching” mechanism in LASV replication.
Shawn Yang, PhD (Georgia State University).
In this Mentored Project, we aim to bring an outstanding young medicinal chemist, Dr. Xiaoxiao (Shawn) Yang, into the field of antiviral research and make impactful contributions to the missions of the Midwest AViDD Center and beyond. We propose to focus on developing endonuclease inhibitors against the Lassa virus, which the Center has designated as a target. The project is a novel supplement to existing programs within the Center. It is likely to succeed because of the FDA approval of an inhibitor, baloxavir, for the same enzyme for the influenza virus. Further, the crystal structure is available, and we have the inhibition assays ready, providing synergy with medicinal chemistry efforts. Yang is mentored by Binghe Wang and Ming Luo (GSU). We expect to identify low-nM inhibitors within a year and then optimize for animal model studies and beyond.
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Endoribonuclease Nsp15
Elisa Fanunza, PhD (University of Cagliari).
The goal of this Mentored Project (MP) is to discover therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2 (SARS2) directed against a less-conventional but attractive target, Nsp15, a virus-encoded endonuclease essential for pathogenesis and evading host immunity. Fanunza aims to deliver direct Nsp15-targeting antivirals that simultaneously block endonuclease activity and restore host innate immune responses. She will identify Nsp15-binding compounds using innovative approaches such as DNA-encoded library technology (DEC-Tec) and virtual screening. Then we will characterize small molecule candidates using binding, biochemical, cell-based, and virus replication assays.
Project participants are confident that studies performed here will achieve the principal goal of identifying a new class of antivirals blocking a critical viral-host interaction: Nsp15-IFN. By combining innovative, precise, and reliable technologies, this Mentored Project will generate candidate potent Nsp15 inhibitors (ideally multiple novel scaffolds) for future studies, including structural biology and animal testing.












